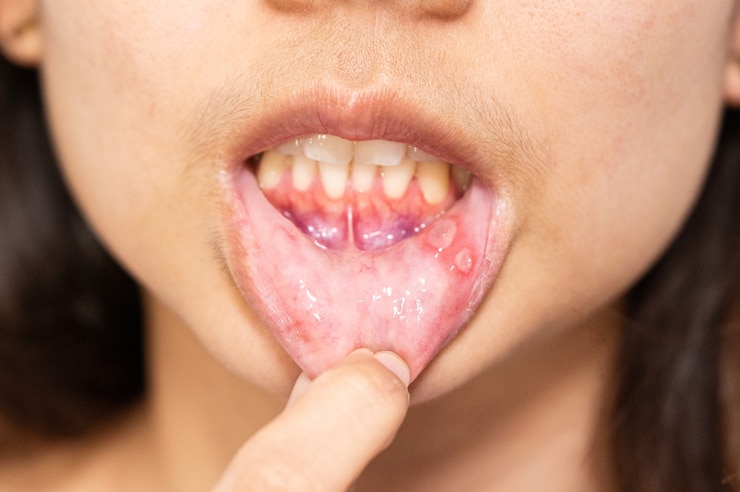
Mouth Ulcers
Mouth ulcers, also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores, are painful lesions that develop on the mucous membranes inside the mouth. They can appear as small, round sores with a white or yellow center and a red halo. These ulcers can vary in size and can affect any part of the oral cavity, including the gums, tongue, inner cheeks, and the roof or floor of the mouth.
Mouth ulcers can arise from various factors, including:
1. Stress: Emotional or physical stress can lead to the development of mouth ulcers.
2. Injury: Minor injuries from dental work, biting the cheek, or aggressive brushing can cause ulcers.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals, particularly Vitamin B12, folate, and iron.
4 Food Sensitivities: Certain foods, such as citrus fruits, nuts, and chocolate, may trigger ulcers in some individuals.
5. Medical Conditions: Conditions like celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders can increase susceptibility to mouth ulcers.
6. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during menstruation, can contribute to the occurrence of ulcers.
1. Stress: Emotional or physical stress can lead to the development of mouth ulcers.
2. Injury: Minor injuries from dental work, biting the cheek, or aggressive brushing can cause ulcers.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals, particularly Vitamin B12, folate, and iron.
4 Food Sensitivities: Certain foods, such as citrus fruits, nuts, and chocolate, may trigger ulcers in some individuals.
5. Medical Conditions: Conditions like celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders can increase susceptibility to mouth ulcers.
6. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during menstruation, can contribute to the occurrence of ulcers.
1. Pain or discomfort, especially when eating, drinking, or speaking
2. Sensitivity to certain foods, particularly spicy or acidic items
3. Swelling and redness around the ulcer
4. A burning or tingling sensation before the ulcer appears
2. Sensitivity to certain foods, particularly spicy or acidic items
3. Swelling and redness around the ulcer
4. A burning or tingling sensation before the ulcer appears
While most mouth ulcers heal on their own within one to two weeks, treatment can help alleviate pain and promote healing. Treatment options include:
1. Topical Medications: Over-the-counter gels or ointments can provide pain relief and protect the ulcer.
2 . Mouth Rinses: Antiseptic or anti-inflammatory mouth rinses can help reduce discomfort and promote healing.
3. Oral Medications: In severe cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe medications to manage pain and inflammation.
4. Nutritional Supplements: If a deficiency is identified, supplements may be recommended to address nutritional gaps.
1. Topical Medications: Over-the-counter gels or ointments can provide pain relief and protect the ulcer.
2 . Mouth Rinses: Antiseptic or anti-inflammatory mouth rinses can help reduce discomfort and promote healing.
3. Oral Medications: In severe cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe medications to manage pain and inflammation.
4. Nutritional Supplements: If a deficiency is identified, supplements may be recommended to address nutritional gaps.
1. Maintain good oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing.
2. Avoid known irritants such as spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods.
3. Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
4. Ensure a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
2. Avoid known irritants such as spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods.
3. Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
4. Ensure a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
1. Are mouth ulcers contagious?
No, mouth ulcers are not contagious. They are usually caused by factors such as stress, injury, or nutritional deficiencies, and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
2. How long do mouth ulcers typically last?
Most mouth ulcers heal on their own within 1 to 2 weeks. However, larger ulcers or those caused by underlying health conditions may take longer to heal.
3. What should I avoid eating if I have a mouth ulcer?
It is best to avoid spicy, acidic, or abrasive foods that can irritate the ulcer and exacerbate pain. Opt for softer, bland foods and stay hydrated.
No, mouth ulcers are not contagious. They are usually caused by factors such as stress, injury, or nutritional deficiencies, and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
2. How long do mouth ulcers typically last?
Most mouth ulcers heal on their own within 1 to 2 weeks. However, larger ulcers or those caused by underlying health conditions may take longer to heal.
3. What should I avoid eating if I have a mouth ulcer?
It is best to avoid spicy, acidic, or abrasive foods that can irritate the ulcer and exacerbate pain. Opt for softer, bland foods and stay hydrated.


